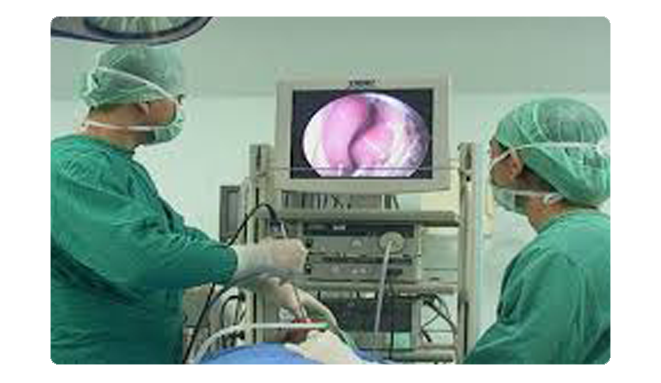
Surgical Services
General surgery is a surgical specialty that focuses on abdominal contents including oesophagus, stomach, small bowel, colon, liver, pancreas, gallbladder and bile ducts, and often the thyroid gland (depending on local reference patterns). They also deal with diseases involving the skin, breast, soft tissue, trauma , peripheral vascular surgery and hernias.
General surgery is a discipline that requires knowledge of and familiarity with a broad spectrum of diseases that may require surgical treatment. By necessity, the breadth and depth of this knowledge will vary by disease category. In most areas, the surgeon will be expected to be competent in diagnosing and treating the full spectrum of disease. However, there are some types of disease in which comprehensive knowledge and experience are not generally gained in the course of a standard surgical residency. In these areas, the surgeon will be able to recognise and treat a select group of conditions within a disease category.
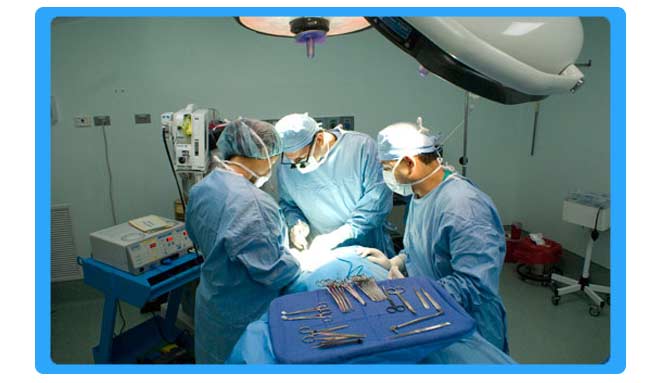
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery (MIS), bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique in which operations are performed far from their location through small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) elsewhere in the body.
There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus the more common, open procedure. Pain and hemorrhaging are reduced due to smaller incisions and recovery times are shorter. The key element in laparoscopic surgery is the use of a laparoscope, a long fibre optic cable system which allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. There are two types of laparoscope telescopic rod lens system, that is usually connected to a video camera (single chip or three chip), or a digital laparoscope where the charge-coupled device is placed at the end of the laparoscope.
Colorectal Surgery
Colorectal surgery is a field in medicine, dealing with disorders of the rectum, anus, and colon. The field is also known as proctology, but the latter term is now used infrequently within medicine, and is most often employed to identify practices relating to the anus and rectum in particular. The word proctology is derived from the Greek words πρωκτός proktos, meaning “anus” or “hindparts”, and -λογία -logia, meaning “science” or “study”.
Physicians specialising in this field of medicine are called colorectal surgeons or proctologists. In the United States, to become colorectal surgeons, these surgical doctors have to complete a general surgery residency, as well as a colorectal surgery fellowship, upon which they are eligible to be certified in their field of expertise by the American Board of Colon and Rectal Surgery or the American Osteopathic Board of Proctology. In other countries, certification to practice proctology is given to surgeons at the end of a 2–3 year sub-speciality residency by the country’s board of surgery.
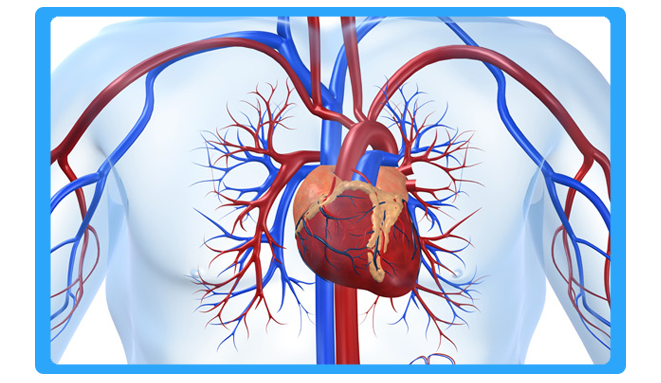
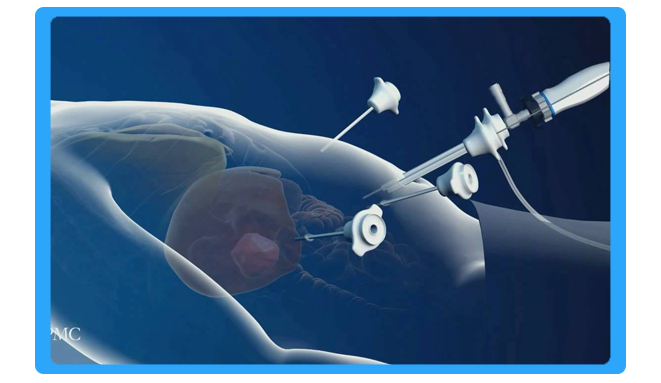
Vascular Surgery
Vascular surgery is a surgical specialty in which diseases of the vascular system, or arteries and veins, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures, and surgical reconstruction. The specialty evolved from general and cardiac surgery as well as minimally invasive techniques pioneered by interventional radiology. The vascular surgeon is trained in the diagnosis and management of diseases affecting all parts of the vascular system except those of the heart and brain. Cardiothoracic surgeons and interventional cardiologists manage disease of vessels of the heart. Neurosurgeons and interventional neuroradiologists manage surgical disease of the vessels in the brain (e.g., intracranial aneurysms).
Vascular surgery encompasses surgery of the aorta, carotid arteries, and lower extremities, including the iliac, femoral, and tibial arteries. Vascular surgery also involves surgery of veins, for conditions such as May-Thurner syndrome and for varicose veins. In some regions, vascular surgery also includes dialysis access surgery and transplant surgery.
Colonoscopy Surgery
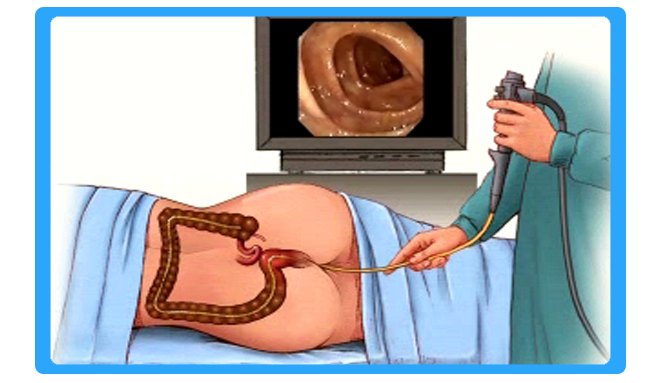
Colonoscopy is a test that allows your doctor to look at the inner lining of your large intestine (rectum and colon). He or she uses a thin, flexible tube called a colonoscope to look at the colon. A colonoscopy helps find ulcers, colon polyps, tumors, and areas of inflammation or bleeding.
Colonoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis (e.g. ulceration, polyps) and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected colorectal cancer lesions. Colonoscopy can remove polyps as small as one millimetre or less. Once polyps are removed, they can be studied with the aid of a microscope to determine if they are precancerous or not. It can take up to 15 years for a polyp to turn cancerous.
Proctoscopy Surgery
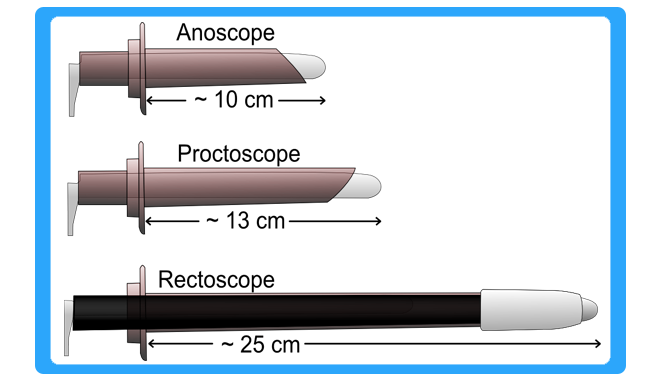
Proctoscopy is a common medical procedure in which an instrument called a proctoscope (also known as a rectoscope, although the latter may be a bit longer) is used to examine the anal cavity, rectum, or sigmoid colon. A proctoscope is a short, straight, rigid, hollow metal tube, and usually has a small light bulb mounted at the end. It is approximately 5 inches or 15 cm long, while a rectoscope is approximately 10 inches or 25 cm long. During proctoscopy, the proctoscope is lubricated and inserted into the rectum, and then the obturator is removed, allowing an unobstructed view of the interior of the rectal cavity. This procedure is normally done to inspect for hemorrhoids or rectal polyps and might be mildly uncomfortable as the proctoscope is inserted further into the rectum. Modern fibre-optic proctoscopes allow more extensive observation with less discomfort.
Fibre optic proctoscopes are now available which cause less discomfort to the patient. The proctoscope is used in the diagnosis of hemorrhoids, carcinoma of anal canal or rectum and rectal polyp. It is used therapeutically for polypectomy and rectal biopsy.
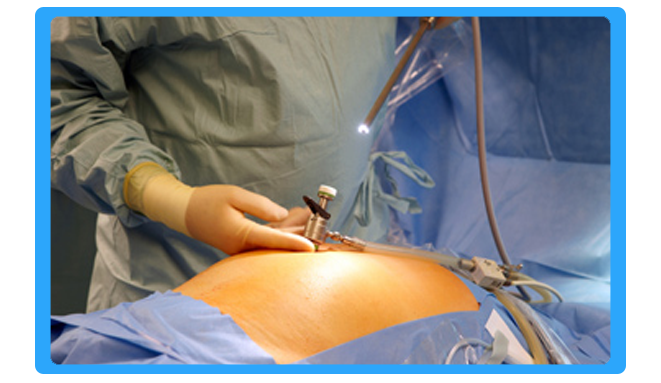
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
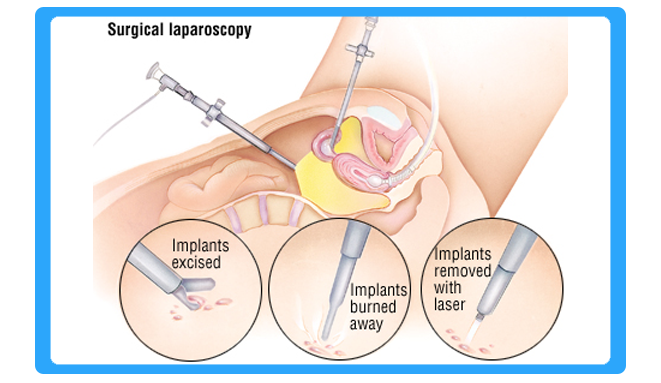
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a surgical procedure that doctors use to view a woman’s reproductive organs. A laparoscope, a thin viewing tube similar to a telescope, is passed through a small incision (cut) in the abdomen.
Laparoscopy, a short procedure done under general anesthesia, is usually performed in a hospital or surgery center. Once the anesthesia takes effect, a needle is inserted into your abdomen and a harmless gas is injected through the needle. The gas raises the abdominal wall so the physician can see your reproductive organs more clearly. Once the gas is inserted, the needle is removed and a laparoscope, a narrow, fiberoptic telescope, is inserted through a tiny incision. A probe, used to move and lift organs to see hidden areas, is inserted through another small incision in your lower abdomen. Scissors may be used to cut out scar tissue, and lasers or electrocautery may be used to treat endometriosis. The injection of dye through the tubes, similar to HSG, may also be performed at this time to detect blockage in the fallopian tubes.
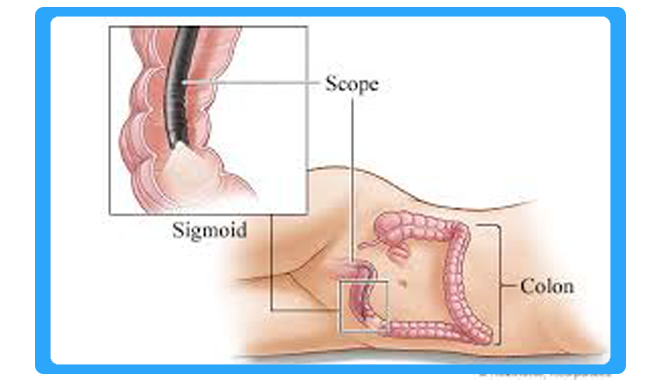
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is the minimally invasive medical examination of the large intestine from the rectum through the last part of the colon. There are two types of sigmoidoscopy: flexible sigmoidoscopy, which uses a flexible endoscope, and rigid sigmoidoscopy, which uses a rigid device. Flexible sigmoidoscopy is generally the preferred procedure. A sigmoidoscopy is similar to, but not the same as, a colonoscopy. A sigmoidoscopy only examines up to the sigmoid, the most distal part of the colon, while colonoscopy examines the whole large bowel.
If anything unusual is in the rectum or colon, like a polyp or inflamed tissue, the physician can remove a piece of it using instruments inserted into the scope. The physician will send that piece of tissue (biopsy) to the lab for testing. Bleeding and puncture of the colon are possible complications of sigmoidoscopy. However, such complications are uncommon. Flexible sigmoidoscopy takes 10 to 20 minutes. During the procedure, the patient might feel pressure and slight cramping in the lower abdomen, but he or she will feel better afterward when the air leaves the colon.
Plastic Surgery
Plastic surgery is a medical procedure with the purpose of alteration or restoring the form of the body. Though cosmetic or aesthetic surgery is the most well known kind of plastic surgery, plastic surgery itself is not necessarily considered cosmetic; and includes many types of reconstructive surgery, craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns.
Reconstructive plastic surgery is performed to correct functional impairments caused by burns; traumatic injuries, such as facial bone fractures and breaks; congenital abnormalities, such as cleft palates or cleft lips; developmental abnormalities; infection and disease; and cancer or tumours. Reconstructive plastic surgery is usually performed to improve function, but it may be done to approximate a normal appearance. Cosmetic surgery is an optional procedure that is performed on normal parts of the body with the only purpose of improving a person’s appearance and/or removing signs of ageing.

ENT Surgery
Otorhinolaryngology (Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, or OHNS) is the area of medicine that deals with disorders conditions of the ear, nose, and throat (ENT) region, and related areas of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, ENT doctors, ENT surgeons, or head and neck surgeons. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, or base of the skull, and for the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors of the head and neck.
One of the key areas of concern for ENT surgeons are helping patients cope with or recover from diseases that impair the senses of hearing and balance. They will also be concerned with the functional aspects of breathing, eating and speech. ENT surgeons also deal with cancers in this region of the body. Many will undertake plastic and reconstructive work on the face.
Arthroscopy Surgery
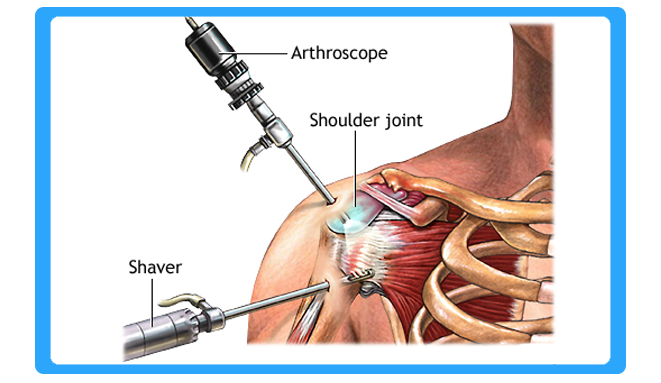
Arthroscopy (also called arthroscopic surgery) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure on a joint in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage is performed using an arthroscope, an endoscope that is inserted into the joint through a small incision.
The advantage over traditional open surgery is that the joint does not have to be opened up fully. For knee arthroscopy only two small incisions are made, one for the arthroscope and one for the surgical instruments to be used in the knee cavity. This reduces recovery time and may increase the rate of success due to less trauma to the connective tissue. It is especially useful for professional athletes, who frequently injure knee joints and require fast healing time. There is also less scarring, because of the smaller incisions. Irrigation fluid is used to distend the joint and make a surgical space. Sometimes this fluid leaks (extravasates) into the surrounding soft tissue, causing edema.
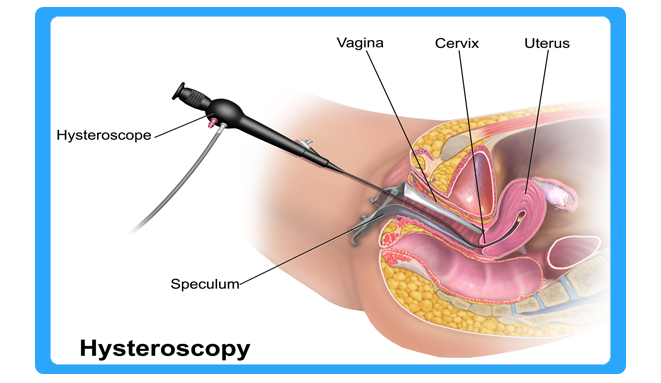
Hysteroscopy Surgery
Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows your doctor to look inside your uterus in order to diagnose and treat causes of abnormal bleeding. Hysteroscopy is done using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted into the vagina to examine the cervix and inside of the uterus.
A hysteroscope is an endoscope that carries optical and light channels or fibers. It is introduced in a sheath that provides an inflow and outflow channel for insufflation of the uterine cavity. In addition, an operative channel may be present to introduce scissors, graspers or biopsy instruments. A hysteroscopic resectoscope is similar to a transurethral resectoscope and allows entry of an electric loop to shave off tissue, for instance to eliminate a fibroid. A contact hysteroscope is a hysteroscope that does not use distention media.
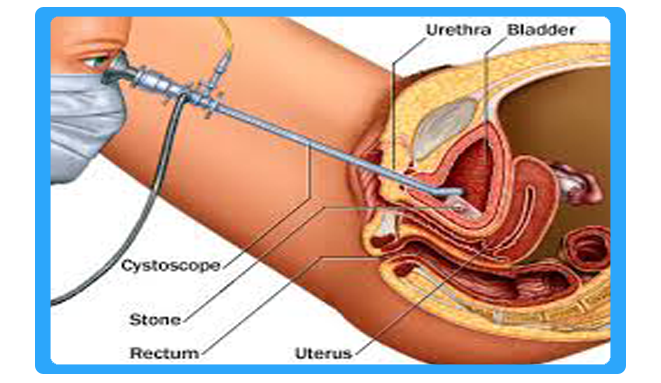
Cystoscopy Surgery
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The cystoscope has lenses like a telescope or microscope.
There are two main types of cystoscopy — flexible and rigid — differing in the flexibility of the cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is carried out with local anaesthesia on both sexes. Typically, a topical anesthetic, most often xylocaine gel (common brand names are Anestacon and Instillagel) is employed. The medication is instilled into the urethra via the urinary meatus five to ten minutes prior to the beginning of the procedure. Rigid cystoscopy can be performed under the same conditions, but is generally carried out under general anaesthesia, particularly in male subjects, due to the pain caused by the probe.
Laryngoscopy Surgery
-
Laryngoscopy is an examination that lets your doctor look at the back of your throat, your voice box (larynx) , and vocal cords with a scope (laryngoscope). There are two types of laryngoscopy, and each uses different equipment.
-
Direct laryngoscopy uses a tube called a laryngoscope. The instrument is placed in the back of your throat. The tube may be flexible or stiff. This procedure allows the doctor to see deeper in the throat and to remove a foreign object or sample tissue for a biopsy. It is done in a hospital or medical center under general anesthesia, meaning you will be asleep and pain-free.
Pharyngoscopy Surgery
A pharyngoscopy is often used to examine the back of the throat. The two types of pharyngoscopy are indirect pharyngoscopy and direct pharyngoscopy.
During an indirect pharyngoscopy your doctor places small mirrors at the back of your mouth to clearly examine your throat, the base of your tongue and part of your larynx.
-
A direct pharyngoscopy involves a fiber optic source that uses a flexible, lighted, narrow tube which may be inserted into the mouth or nose so that your doctor can examine hard-to-see areas such as the larynx and behind the nose.